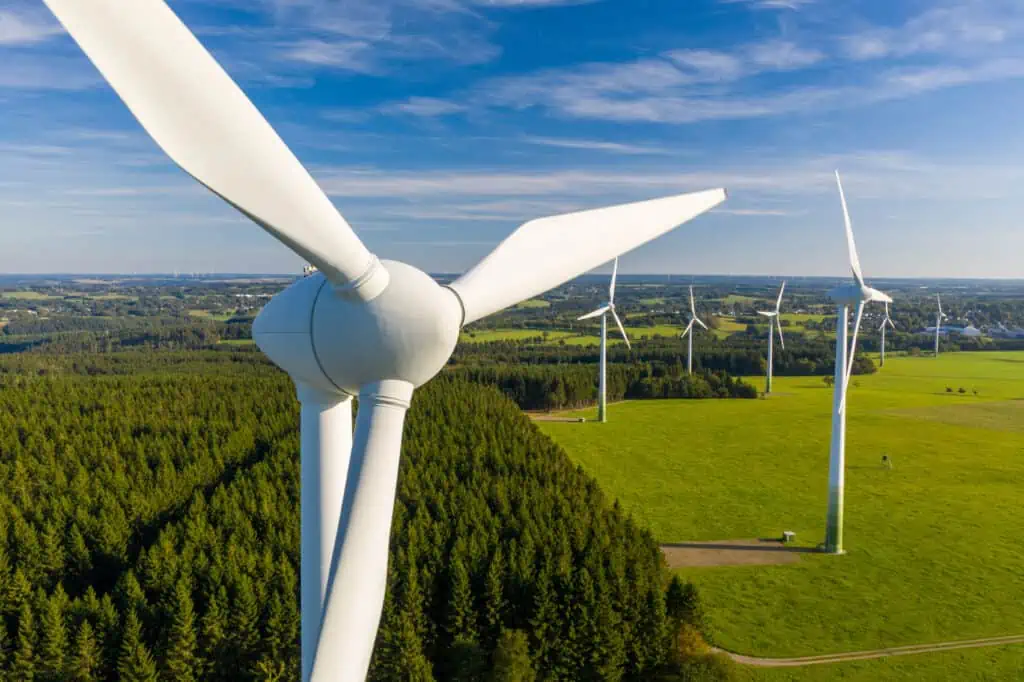
Wind turbines harness the wind’s kinetic energy through the use of blades. As the wind passes over the blades, it generates lift, much like airplane wings, causing the blades to rotate. These rotating blades are linked to a drive shaft that powers an electric generator to produce electricity.
Where does wind come from?
Wind energy is generated by the movement of air, which is primarily a result of the sun’s uneven heating of the Earth’s surface. Variations in the composition of land and water on the Earth’s surface lead to differential absorption of solar heat resulting in what we call wind.

Electricity Generation from Wind
In the United States, annual wind energy generation increased from approximately 6 billion kWh in 2000 to around 380 billion kWh in 2021. By 2022, wind turbines accounted for about 10.2% of total U.S. electricity generation.
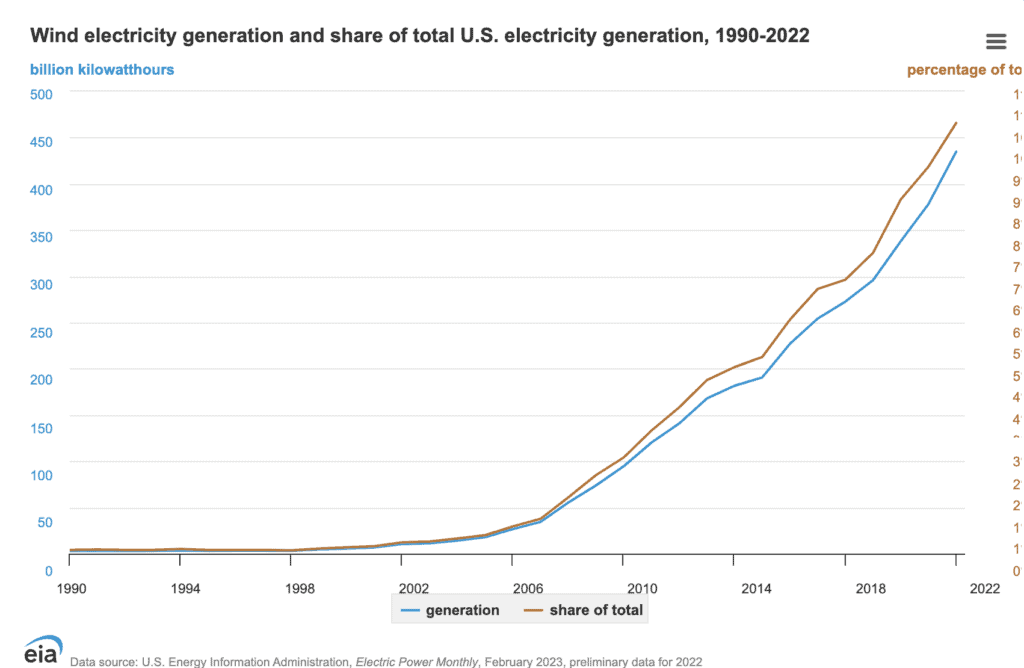
This has been thanks to advancements in wind energy technology and lower generation costs. Government mandates and financial incentives promoting renewable energy have also played a role in this expansion.
Where is Wind Power Generated?
In 2023, the majority of U.S. wind electricity generation capacity has been in the central part of the country with states like Texas, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas and Illinois.
There are also offshore wind energy projects are being developed along the East Coast, taking advantage of the region’s wind energy. Currently, there are two operational projects in Rhode Island and Virginia. Other projects in state and federal waters along the East Coast, including Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Rhode Island, and Virginia, are in different stages of planning and development.
Negative Impacts of Wind Farms
Wind turbines have certain negative environmental impacts such as rare incidents of fires and fluid leaks. Wind turbine blades can harm birds by collisions with the blades, potentially impacting their populations.
Additionally, land-based wind projects may require service roads, further impacting the environment. The production of materials for wind turbine components has environmental consequences, and some fossil fuels are used in this process. While many materials can be reused or recycled, most turbine blades cannot be recycled. However, research is being done for ways to make blades recyclable and reduce manufacturing energy requirements.
Positive Impacts of Electric Generation from Wind Turbines
Wind is a clean and renewable energy source with minimal environmental impact. Wind turbines do not emit pollutants and don’t need water for cooling. They can also reduce reliance on fossil fuels, leading to lower air pollution and carbon emissions.
