It is no secret that electricity is the lifeblood and backbone of our society.
Without it, our society would be lost in the dark. In order to take full advantage of electricity when purchasing it, it is vital to understand how it all works and how aspects of its generation affect pricing.
Key Takeaways:
- A brief history of electrical generation
- The different turbine technologies for electricity generation
- Breakdown of US electricity generation by source
- The selling of electricity generation
- How electricity generation affects electricity rates
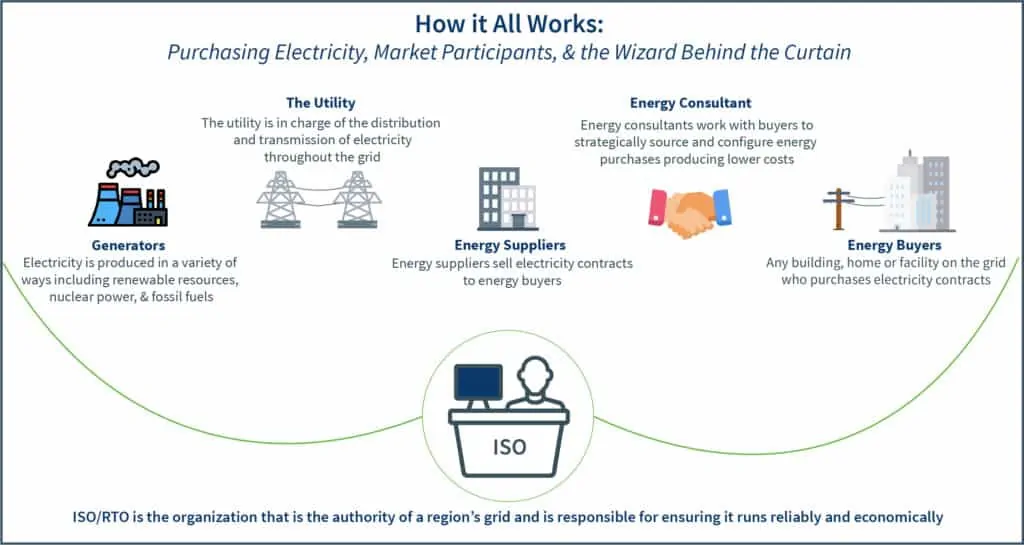
In our previous Energy 101 post, we talked about the organization in charge of the entire electricity grid to ensure everything runs reliably and smoothly, the ISO. In this post, we will be taking our journey further, or rather, to the beginning of it: generation.
Where exactly does electricity come from, how does it get generated, and how does it affect your rates? Read on to find out!
A Brief History of Electricity Generation
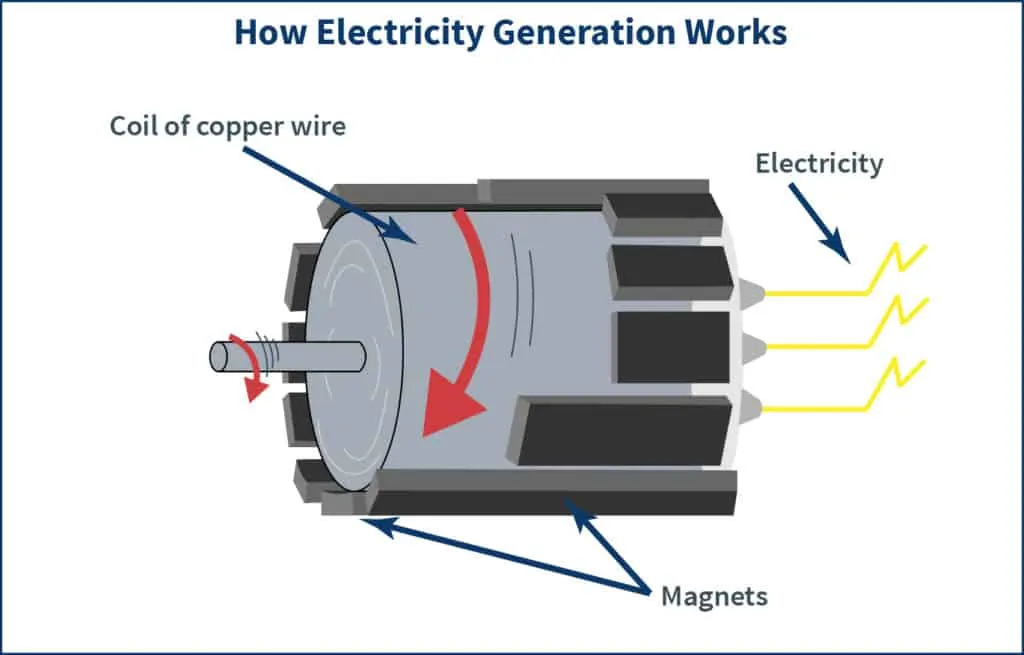
When discussing the origins of modern electricity, most choose to talk about Nikola Tesla and Thomas Edison. However, when it comes to our modern way of generating electricity to power homes and businesses on the grid, the person we should thank is an English scientist by the name of Michael Faraday.
In the 1800s, Faraday discovered a way to generate electricity currents. He did this by moving a loop of copper wire rapidly around both poles of a magnet. While this invention may seem rudimentary, it is the basis for how we generate electricity using turbines today!
Power Stations and Power Plants
Once this discovery was made, governments saw the value and began mass-producing it. In order to generate electricity on a grand scale and provide it to all homes and businesses on a grid, they started developing power stations & power plants all across the country. This is still how we generate electricity we use in our homes and businesses today.
Some of these plants are very large and cover a large geographical region while others are fairly small and cover only a limited area. Regardless of the size, the majority of these power plants rely on turbine technology that use Faraday’s process to create the amount of electricity needed to service their area.
Generating Electricity Using Turbines
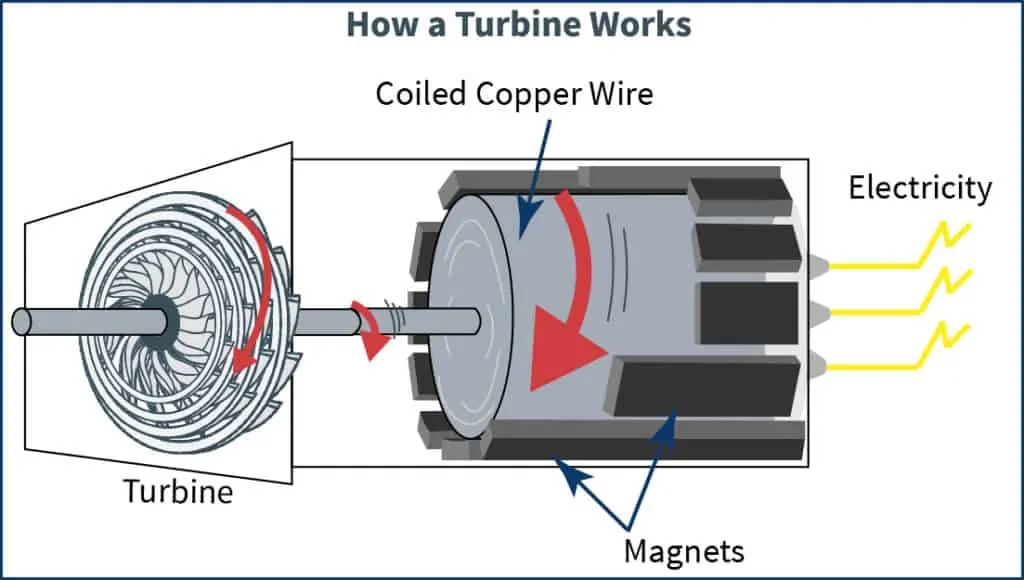
Turbines are large devices that transform kinetic energy into electricity. Put simply, this is the idea of using mechanical energy to force a generator to rotate. Albeit on a much larger scale to allow for continuous motion for long periods of time, turbines use the basis of Faraday’s process i.e. rotating a magnet within loops of conduction material like copper wire!
Although it seems like ancient technology at this point, this is still how most of commercial electricity is generated today!
While the most common turbines are powered by fossil fuels like natural gas and coal, renewable energy sources drive turbines by using fuel like wind, water, and even tidal power.
Regardless of the fuel source, the generation process of turning mechanical energy into electricity is the same: turbines drive a spinning magnetic field of static coils of wire.
Types of Turbines
Turbines are the most common method of generating electricity. This is because they have the ability to produce the greatest amount in a safe and reliable way. Below are a few of the main types of turbines and a brief description of how each works.
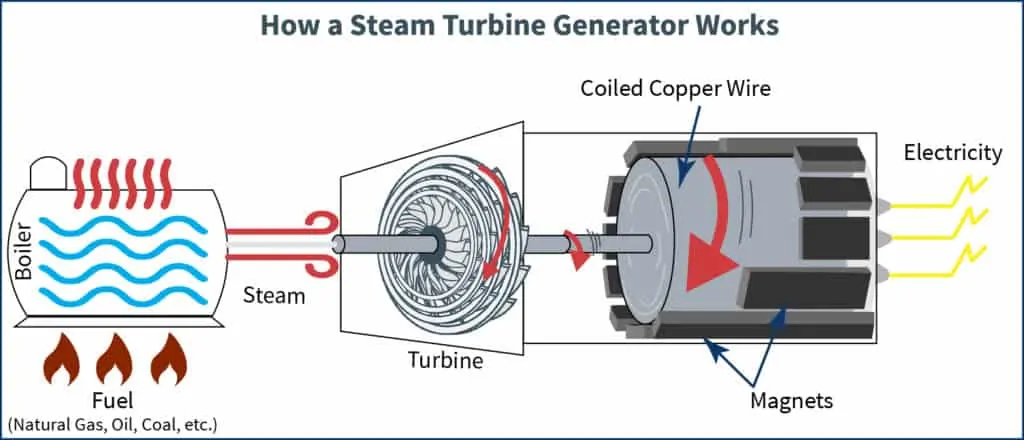
Steam turbines work by removing thermal energy from a fuel source to transform water into steam. The steam that is created is used to turn the turbines. There are a variety of fuel sources that rely on steam to turn turbines to produce electricity.
Fossil fuels plants use sources like coal, oil, and natural gas to heat water, which creates steam that turns a turbine. While these resources have seen a decline in usage over the last few years, they are still some of the most common electricity generation resources.
Nuclear plants also work this way, although using a significantly more complicated method. These plants use a process called nuclear fission to split atoms of uranium to generate extreme pressure and heat. Because the uranium fuel is surrounded by water, when the atoms are split, they release neutrons and heat which creates the steam that powers the turbine and generator.
There are also renewable energy sources that use steam to power turbines such as solar thermal energy, geothermal power, and biomass.
Gas turbines work by igniting natural gas to produce pressure, which turns the turbine. As stated above, natural gas can also be used to heat water and generate steam, which then turns the turbine to generate electricity.
These are important because the ISO may call upon them if they need more electricity than they expected as they can ramp up generation quicker than most other turbines.
There are also combined cycle turbines that use both gas combustion as well as steam turbines to generate electricity. These turbines produce 50% more electricity from their fuel than a single-cycle power system like described above.
Combined cycle turbines generate power in two stages.
First, a gas turbine burns natural gas and uses that heat to turn a turbine. Then, the residual heat from the gas turbine is sent into a heat recovery steam generator where it boils water to produce steam. This steam is then used to turn an additional steam turbine generator, producing more electricity. The steam is then condensed back into water and is recycled through the system.
Watch this Tennessee Valley Authority video below to see how combined cycle turbine generators work in action.
A renewable energy source, wind turbines rely on wind to turn large blades to create mechanical energy. This rotation turns gears inside the device extremely fast, which spins a generator that produces electricity.
The large versions of these, often seen grouped together in the ocean or in large fields, contribute to the domestic power supply. Because too much power to fuel their region is often produced, these ones often sell unused power back to the utility through the grid.
Another renewable resource, hydroelectric turbine generators use the movement of water to turn turbines. This includes falling water like in dams as well as the rise and fall of ocean tides, or even ocean thermal currents.
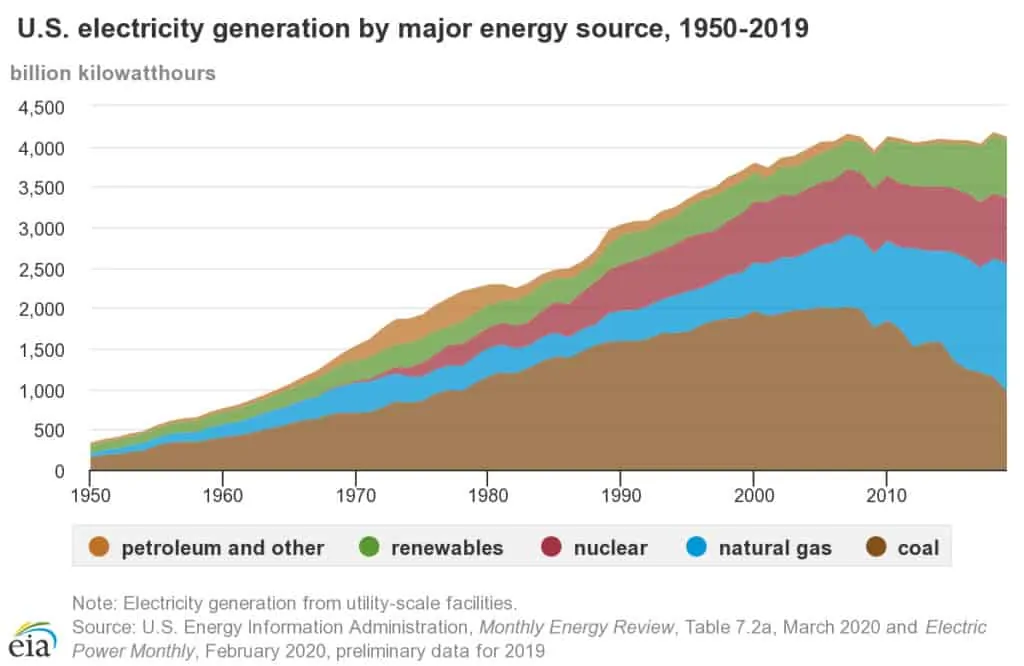
United States Electricity Generation by Source
As you can see from the above, most electricity is generated using steam turbines. However, we can break the sources of electricity generation in the United States into 3 major categories: fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable energy.
The portion of this generation is constantly changing.
Fossil Fuels
While they are declining in popularity, the largest fuel source of electricity generation is still fossil fuels.
In 2019, natural gas accounted for 38% of all electricity generation. This includes both steam-powered turbines as well as gas turbines.
Coal was the second highest energy source at about 23%. The vast majority of coal-fired power plants rely on steam turbines.
Petroleum, on the other hand, accounted for less than 1% of electricity generation in 2019. Some steam turbines are powered by residual fuel oil and petroleum coke. However, these can also be burned in gas turbines.
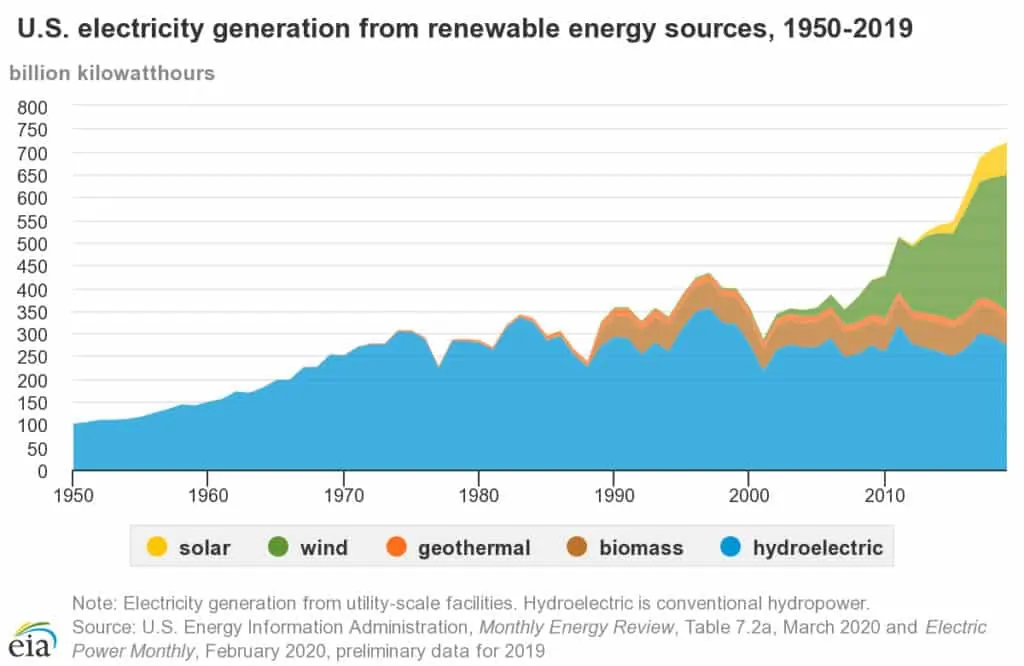
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy has experienced a pretty large explosion in usage climbing to 17% of total generation in the US in 2019. This is in part due to subsidies applied to the usage of them to provide more clean fuel for homes and businesses.
In fact, the renewable energy portion of many electricity bills is increasing yearly as suppliers are required to have a percentage of their electricity supply come from renewable resources.
- Wind turbines: Accounted for 7% of the total US power generation in 2019 and 42% of all renewable electricity generation.
- Hydropower Plants: Produced about 7% of total electricity generation in the US in 2019 and accounted for about 38% of all renewable electricity generation.
- Geothermal Power Plants: Generated about 0.5% of total US electricity generation.
- Solar Energy: Provided 2% of total US electricity generation.
- Biomass: Supplied about 1% of total US electricity generation.
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy has grown in recent years to be about 20% of all generation in 2019. While not a renewable resource, nuclear energy is one of the most clean burning fuels as it produces the least amount of air pollutants.
How Generators Sell Electricity
So how do generators sell the electricity they produce?
First, generators must secure the necessary approval to connect to the grid so they can provide electricity to it. Once this is in place, generators sell their ability to produce electricity at an auction run by the ISO or RTO in their area.
Each day the ISO lets generators know the amount of electricity they expect they will need to power their grid the following day. The generators then provide the ISO bids that say they will produce X MW of electricity at Y price for Z hour. For instance, a power plant that can produce 1,000 MW of electricity per day might place a bid that says they will provide 30MW at 11am at $40 per MWH.
Every generator connected to the grid is required to bid on what they can produce for each hour, unless they are unable to due to legitimate maintenance issues. When the ISO selects a generator’s bid, it is called the ‘clearing price’. Each generator that bid at the clearing price or below it is required to produce the amount of electricity for the specific hour they said they would in their bid.
For example, if the generator’s bid that was selected for 9am to 10am was $40 per MWH produced, this would be the clearing price. Each generator that placed a bid for 9am that was at or below $40 will be paid $40 per MWH that they produce and send to the grid.
In turn, every load serving entity (LSE) i.e. suppliers, utilities, basic service, etc., ends up paying the clearing price for the electricity contracts they sell. This cost is eventually passed down to the residents and businesses that purchase these supplier contracts. This is referred to as the retail market.
The price end users pay in the retail market for electricity can be agreed upon years ahead of time through energy contracts, which often results in avoided costs.
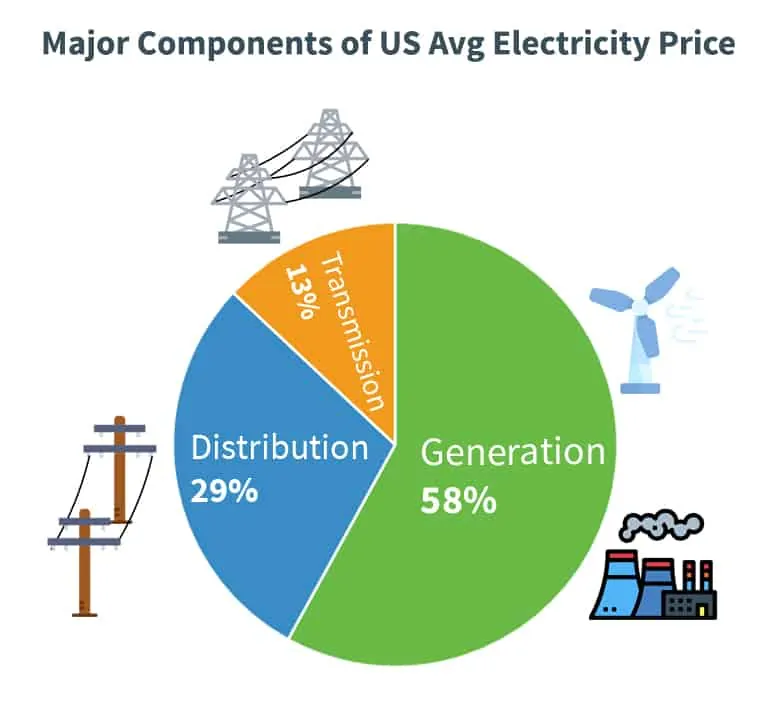
Electricity Generation’s Effect on Prices
The rates businesses and residents pay for electricity are impacted by a variety of factors. One of these is electricity generation and, in 2019, it occupied over 50% of the total US average price of electricity!
To ensure reliability, power plants require a great deal of maintenance to keep everything running smoothly. This is a critical aspect of power plants as their generation equipment needs to constantly be working at an optimum capacity. There is also the cost of construction and operation of these plants.
That being said, the biggest factor in determining a price is the price generators pay for their fuel to produce electricity. For instance if the price for natural gas, one of the most popular electricity generation fuels, goes up, electricity generation plants that use natural gas as fuel will pay more for it and will often make their bid reflect that. When these bids are accepted, this clearing price is passed down to suppliers and, in turn, end users.
This is why watching the natural gas market is so important when determining how electricity prices will move, especially in New England!
So, now you understand how electricity is generated, how it is purchased by LSEs, and how it affects the price you pay for electricity!
There are two important things to takeaway from this post:
- The price of natural gas is a massive mitigating factor in the price of electricity, especially in New England.
- The generation required from renewable sources is increasing significantly! Just look at what happened to electricity prices in Massachusetts when suppliers were required by law to increase the portion of renewable energy in their electricity supply price in this client story.
Check out all of our Energy 101 series of posts to increase your understanding of the complicated world of energy. In our next one, we will be talking about utilities and the distribution and transmission of electricity from generators to the electricity grid so be sure to watch out for updates on this blog or by following us on LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter.
To learn more about electricity generation, why it is important for your business, and how to purchase intelligently to avoid costs impacted by it, contact us today.